Differentiating spatial from environmental effects on foliar fungal communities of Populus trichocarpa
Abstract
Aim: Foliar fungi – pathogens, endophytes, epiphytes – form taxonomically diverse communities that affect plant health and productivity. The composition of foliar fungal communities is variable at spatial scales both small (e.g. individual plants) and large (e.g. continents), yet few studies have attempted to tease apart spatial from climatic factors influencing these communities. Moreover, few studies have sampled in more than 1 year to gauge interannual variation in community structure.
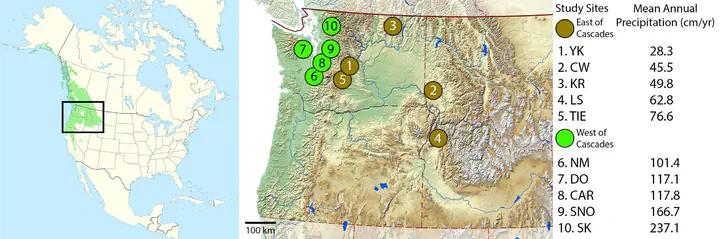
Location: The Pacific Northwest of western North America.
Taxon: Foliar fungi associated with the deciduous tree Populus trichocarpa.
Methods: In two consecutive years, we used DNA metabarcoding to characterize foliar fungal communities of Populus trichocarpa across its geographic range, which encompasses a sharp climatic transition as it crosses the Cascade Mountain Range. We used multivariate analyses to (a) test for and differentiate spatial and environmental factors affecting community composition and (b) test for temporal variation in community composition across spatial and environmental gradients.
Results: In both study years, we found that foliar fungal community composition varied among sites and between regions (east vs. west of the Cascades). We found that climate explained more variation in community composition than geographic distance, although the majority of variation explained by each was shared. We also found that interannual variation in community composition depended on environmental context: communities located in the dry, eastern portion of the tree’s geographic range varied more between study years than those located in the wet, western portion of the tree’s range.
Main conclusions: Our results suggest that the environment plays a greater role in structuring foliar fungal communities than dispersal limitation.